The rapid growth of eCommerce has been a double-edged sword. On the one hand, no borders exist for customers. Marketplaces are getting better and faster, shipping is almost instantaneous, and even returns can be done easily. But on the other hand, with the ease of setting up a marketplace, it has become more difficult to win against the competition. One area that can impact your competitive advantage is your choice of eCommerce platform.
Selecting the right platform is critical and may directly impact your future business strategy and growth initiatives. Many businesses find themselves deciding between Magento or Shopify two of the world’s most popular eCommerce platforms according to Statista. Determining the best platform for your needs can be a complicated process. To help, we have highlighted the top 7 differences between the two technologies.
Both Magento 2 and Shopify have specific advantages, and one may be a better fit than another in certain cases. Researching both to make an informed decision is the business’ responsibility. Use this post as another data point to help you uncover differences that may matter to your business and help guide your decision-making.
How to start?
Model of Delivery
Magento is an open-source eCommerce platform that gives you access to its source code to make changes. This means that after the installation process, merchants are free to make any code changes necessary to better apply the platform to address specific use cases. The open-source software model has grown in popularity and offers many benefits including a large community of developers and the flexibility of nearly endless customization options. As with most open source technologies, customization does require a high degree of technical expertise or the engagement of an external team of developers.
In contrast, Shopify is an off-the-shelf eCommerce platform. It means that the merchant works within the standards of the platform as developed. Shopify delivers automatic updates, security patches and other technical infrastructure through its internal research and development efforts. This more traditional software model has its benefits, but as the eCommerce business grows, limitations of the closed source technology may appear. Platform support response times could be slow, merchants are limited by the functionality on the Shopify roadmap. This means that any process or capability change to the eCommerce site needed by the business has to go through the filter “Does Shopify support this?”
Cost of Ownership
Cost of Ownership or Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a critical measure of any business investment. In this case, the definition means the total of all costs that a merchant spends to implement and maintain their eCommerce Platform. What are those costs? Let’s see:
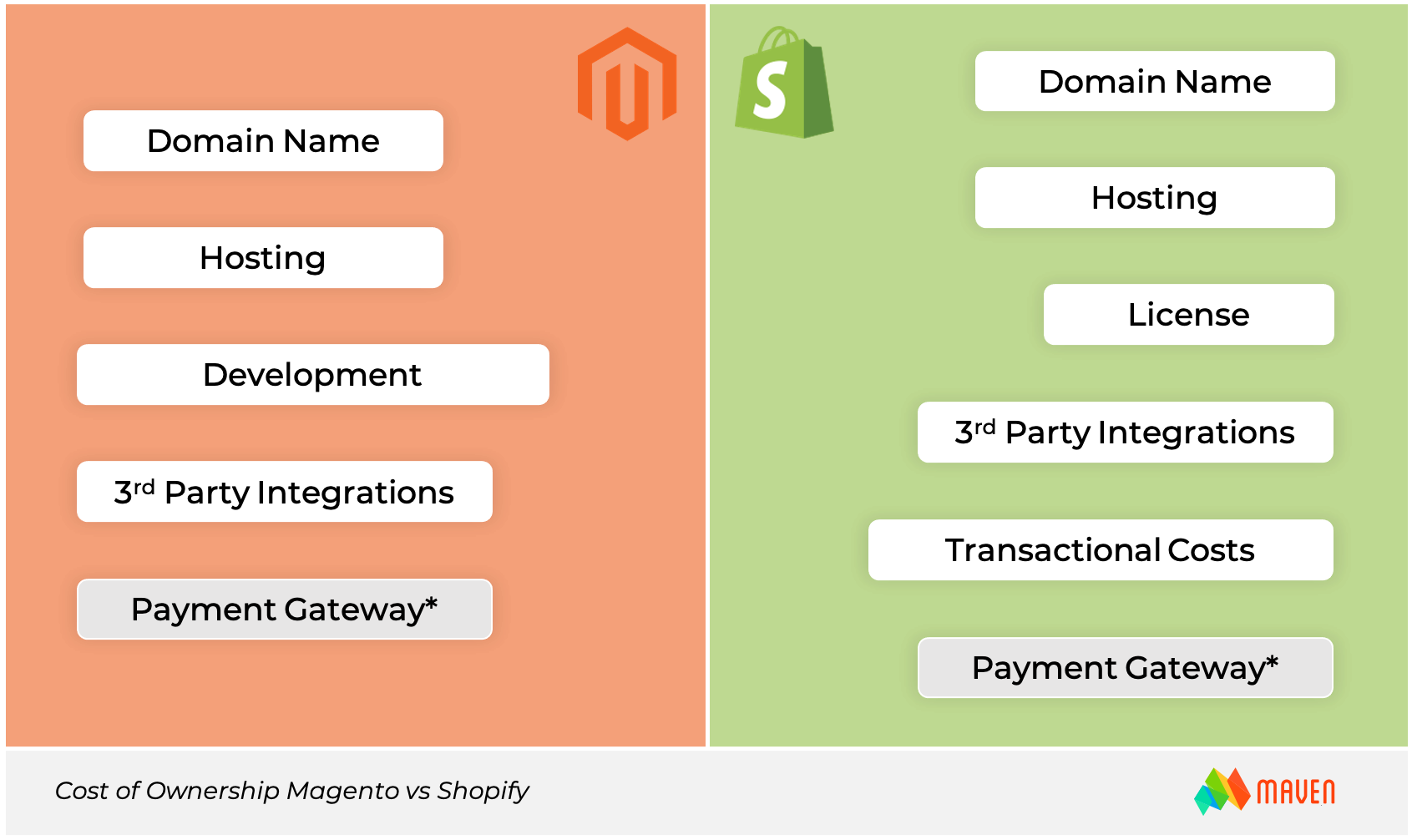
- License fee. Shopify is a closed source platform and uses a subscription model. The price starts at $29/month and goes all the way to $299/month (see the latest pricing). On other hand, Magento is open source and for regular users, it is no need to pay for a license. At the enterprise level, the platforms are relatively the same. Magento Commerce costs $22000/year, and Shopify Plus costs $24000/year.
- Transaction fees. Based on the plan level, Shopify charges merchants an additional fee for each payment made with Shopify Payments. Fees start at 2.9% + 30c per transaction on a basic plan. By contrast, Magento does not charge these fees.
- Integrations. Both Magento and Shopify offer add-on capabilities. Magento calls them “extensions” and Shopify calls them “apps”. The price for both Magento extensions and Shopify apps could be as low as $30 and up to $1000 or $2000, making those add-on costs similar between the 2 platforms.
- Domain name and hosting. With either platform, the merchant pays for a domain name on their own. Hosting is a different story. The Shopify subscription includes hosting, eliminating the need for additional or 3rd party hosting services. By contrast, Magento does not offer a hosting option, so the merchant needs to purchase it additionally.
- Development. As mentioned previously, Magento requires a certain level of technical expertise to properly implement. You will need to work with a development team. With Shopify, the merchant does not need to hire an extra team but a concern is the long-term scalability of capabilities and features. Will Shopify be equipped to address and support your business growth over the next 5 years?
Related Post: eCommerce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) or How Much Does an Online Store Cost?
Service Providers
Magento started in 2008, and today boasts a large ecosystem of service providers. It is easy to find an experienced Magento professional in any part of the world. Shopify started a few years earlier, in 2004, so the situation is pretty much the same. The difference between the two is that Magento, as an open-source technology, can be more complex and requires high levels of proficiency. This means that the service provider you choose must be experienced. With either eCommerce platform, take your time and ask detailed questions during the pre-sale phase of the development.
Magento also has a large development community with active forums. For example, StackOverflow is full of fixes, advice and guides. This can be useful for minor changes or simply to learn more about the product.
Functionality
Product Types
Magento has 7 different product types (Simple, Configurable, Grouped, Virtual, Bundle, Downloadable and Gift Card), while Shopify has only one – Simple. Why is it so important?
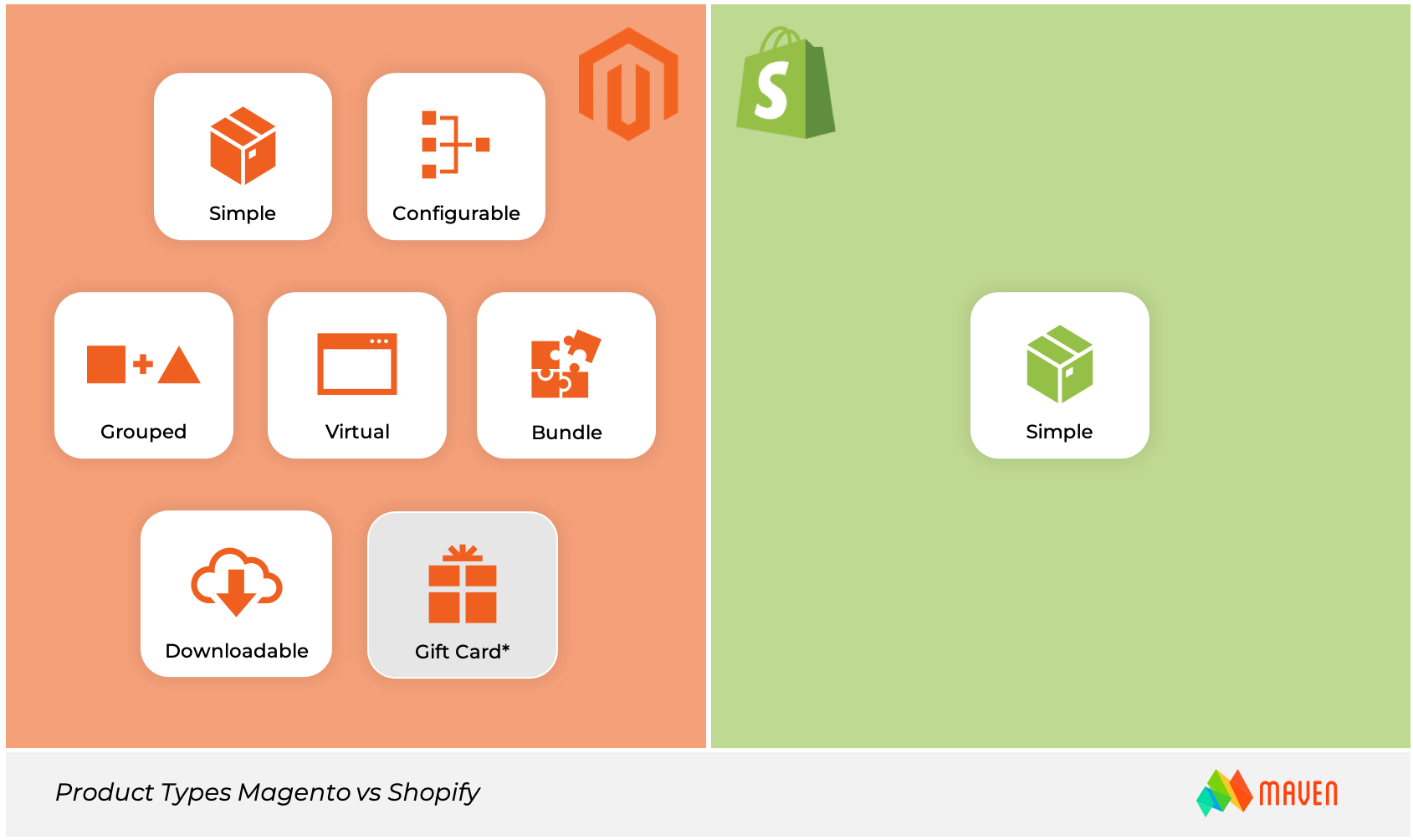
Multiple product types give merchants more configurable options and improve the overall customer experience. It increases the flexibility of the business and allows merchants to sell everything they can imagine online. This includes simple products and complicated product configurations with the customization and different purchase options.
For example, consider a clothing eCommerce site that wants to sell both a single outfit, like a men’s suit, or parts of that outfit, such as the jacket or pants. Shopify would struggle to support that, but Magento is built for these scenarios.
Related Post: Get Familiar With All Types of Magento Products
Multiple Stores
Shopify’s licensing is such that 1 instance = 1 license. A merchant hosting multiple online stores would need to purchase additional licenses. This would also be the case for additional store-fronts as the licensing supports 1 store-front per license.
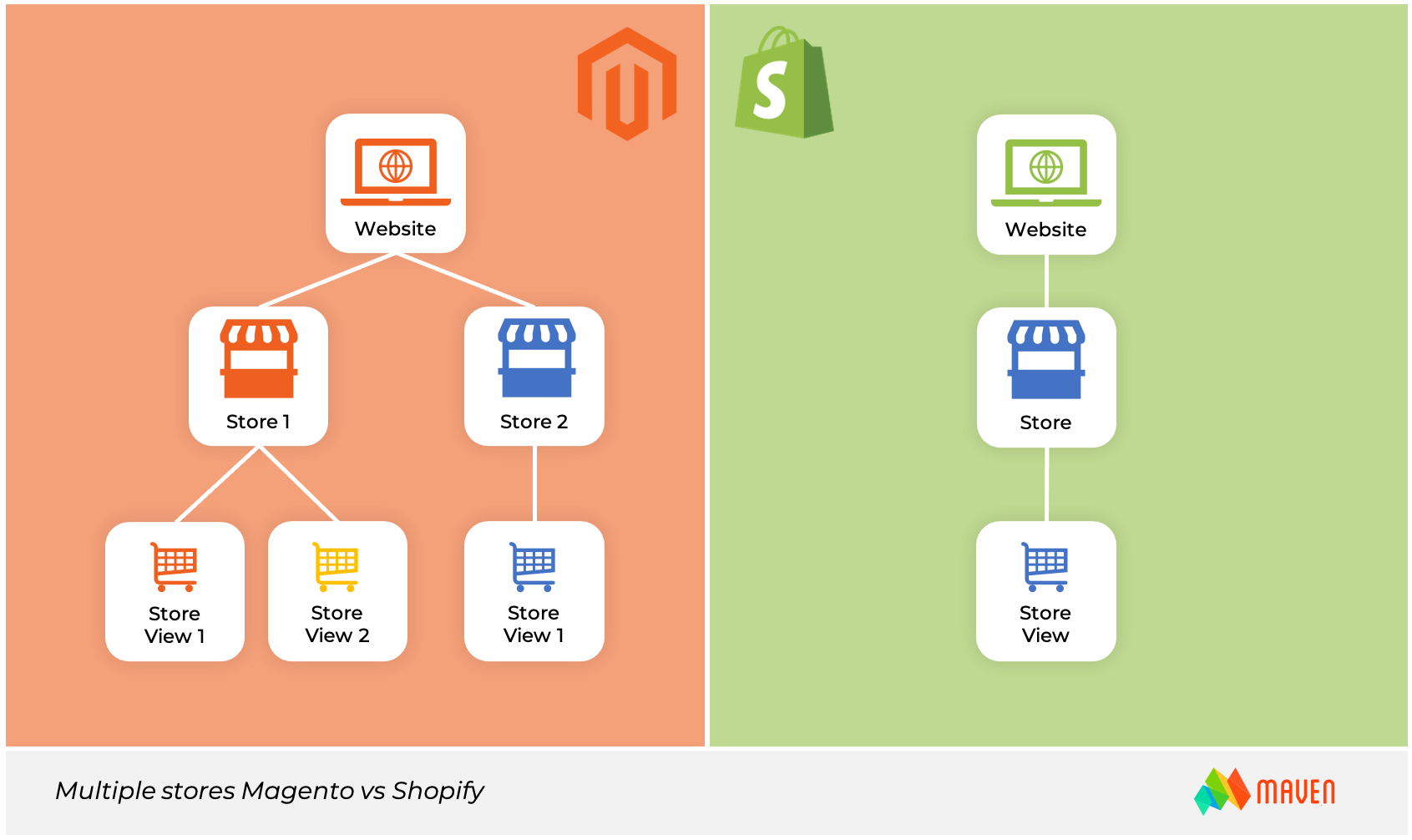
The number of stores and store-fronts available in Magento is unlimited. This capability could make the life of a merchant much easier when the business starts to grow. From a single administration panel, the merchant can manage different websites, store-fronts and catalogs. International shipping, taxing variations, currencies and payment methods are available out-of-the-box. To understand the importance of this difference, let’s review an example.
Let’s say you are a manufacturer of goods from Spain who wants to sell to Germany. By the law of the EU (Europe Union), you need to create another version of the store for Germany with the .de domain. But what if you next want to sell to the Netherlands? Magento is a much more cost-effective choice in this scenario.
Related Post: The Difference Between Magento Store View, Website and Magento Multi-Store
Customer Groups
Another cornerstone difference between Magento and Shopify is the management of customer groups. Shopify allows merchants to tag customers. This feature has very limited functionality and is used mostly for marketing purposes.
Magento, by contrast, offers extensive customer group functionality. Businesses can create different prices for wholesale customers or for those who performed some required steps. Grouping customers helps with taxation, B2B clients, marketing campaigns and much more.
B2B
For the needs of B2B eCommerce Shopify offers Shopify Plus. It is an enterprise version of Shopify, which costs $24000/year. Shopify Plus includes personalized support, a set of features for a wholesale channel and advanced integrations. Unfortunately, Shopify Plus was initially designed for advanced B2C businesses, not B2B, and currently lacks some key capabilities B2B customers need. While B2B companies may be able to operate with the existing functionality, at the end of the day they will find that Shopify is not currently able to address some of the complex requirements of the B2B eCommerce model.
On the other hand, Magento has key features for B2B customers. A significant portion of critical B2B functionality is built-in and available out-of-the-box. Features like customer groups, multi-store and so on are available to simplify configuration for the businesses. The open-source nature of Magento also allows the business to expand on these features. Businesses are encouraged to develop custom capabilities to meet specific B2B needs without paying a license fee. The Enterprise version of Magento has B2B features built-in natively that align to B2B eCommerce best practices.
Related Post: Magento Community vs. Enterprise: which one fits my business?
Summing Up
Both Shopify and Magento are market leaders in eCommerce. While they have significant differences and approaches to managing eCommerce, both offer clear benefits to certain business scenarios. Shopify and its SaaS-based subscription model streamline the process to start an online-store in the short–term. On the other hand, Magento and its open-source platform offer more capabilities out-of-the-box and are more scalable and customizable in the long-term.
By first clearly understanding your business’ current and long-term needs, You’ll be able to make the best product decision for your business.
Your blog so nice I appreciate you for the great job
This was a very meaningful post, so informative and encouraging information, Thank you for this post.
Great to hear that. Thank you!
I always go for Magento as it is easy to use and have more function and features as compare to shopify. Do let me know if anyone is agree with me.
We agree with you! Magento is a great choice!
It’s an interesting subject. I think one of the advantages of Magento is that you own your store, whereas with Shopify if you stop paying the monthly amount, you lose everything.
That’s right!
Thank you for sharing such an informative and encouraging post with us.
You’re very welcome
Great Post!Thank you for sharing this insightful comparison between Magento and Shopify.
Thank you, we are happy to be helpful!